U.S. President Barack Obama and his political opponents in Congress are moving a bit closer to reaching a compromise over contentious year-end financial issues.
No deal appears imminent, but officials say the leader of the Republican-controlled House of Representatives, Speaker John Boehner, met again with the president at the White House. For the first time Boehner offered to let taxes increase for wealthy households earning more than $1 million a year and to raise the country's borrowing limit.
Obama, the Democrat re-elected last month to another four-year term, campaigned to push taxes higher on couples with annual incomes of more than $250,000, but Boehner's offer suggests the two sides may yet be able to reach an agreement.
Despite the possibility of movement in the negotiations, the two sides remain divided on what spending cuts the White House might agree to implement.
Obama is calling for $1.4 trillion in higher taxes during the next decade, with Boehner offering $1 trillion. Obama's Republican opponents are calling for sharp spending cuts in popular government health programs for the elderly and poor, and pensions for older Americans.
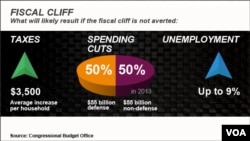
The president and Boehner are trying to avert what Washington is calling a "fiscal cliff," about $500 billion in mandated spending cuts and tax increases that would affect almost all U.S. workers starting January 1, unless they agree on a new financial plan. Analysts say that without a compromise, the shock of the spending trims and higher taxes could send the U.S. spiraling into its second recession in three years.
The United States is also likely to reach its borrowing limit of $16.4 trillion by February and would then run out of money to pay some bills. Mr. Obama wants to increase the borrowing limit as part of the year-end deal, and Boehner offered an unspecified increase in the debt ceiling that would put off a renewed debate on the issue for a year.
Some information for this report was provided by AP, AFP and Reuters.
No deal appears imminent, but officials say the leader of the Republican-controlled House of Representatives, Speaker John Boehner, met again with the president at the White House. For the first time Boehner offered to let taxes increase for wealthy households earning more than $1 million a year and to raise the country's borrowing limit.
Obama, the Democrat re-elected last month to another four-year term, campaigned to push taxes higher on couples with annual incomes of more than $250,000, but Boehner's offer suggests the two sides may yet be able to reach an agreement.
Despite the possibility of movement in the negotiations, the two sides remain divided on what spending cuts the White House might agree to implement.
Obama is calling for $1.4 trillion in higher taxes during the next decade, with Boehner offering $1 trillion. Obama's Republican opponents are calling for sharp spending cuts in popular government health programs for the elderly and poor, and pensions for older Americans.
The president and Boehner are trying to avert what Washington is calling a "fiscal cliff," about $500 billion in mandated spending cuts and tax increases that would affect almost all U.S. workers starting January 1, unless they agree on a new financial plan. Analysts say that without a compromise, the shock of the spending trims and higher taxes could send the U.S. spiraling into its second recession in three years.
The United States is also likely to reach its borrowing limit of $16.4 trillion by February and would then run out of money to pay some bills. Mr. Obama wants to increase the borrowing limit as part of the year-end deal, and Boehner offered an unspecified increase in the debt ceiling that would put off a renewed debate on the issue for a year.
Some information for this report was provided by AP, AFP and Reuters.