WASHINGTON —
On October 14th, 1962, pictures taken by an American U-2 spy plane revealed the presence of Soviet nuclear weapons in Cuba.
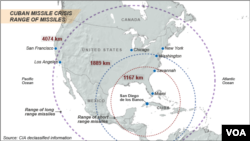
Graham Allison, an expert on the Cuban Missile Crisis, said there were two types of missiles. “One were medium-range ballistic missiles, which could deliver a nuclear warhead at D.C. [District of Columbia],” he said. “And there were intermediate-range nuclear missiles that could deliver warheads as far as Omaha, [Nebraska], where the Strategic Air Command [was located]. So these covered two-thirds of the United States.”
Allison said the discovery was made by what he called “a magical intelligence capability”. “That an airplane, the U-2, could fly at over 60,000 feet, nobody would know that it was there, over territory, and then with this amazing camera take pictures that gave you details of what was happening on the ground - this was just unimaginable for most people. It was a great American intelligence success because the missiles were discovered before they were operational,” said Allison.
Kennedy Discusses Options
President John F. Kennedy then convened a small group of experts to decide what course of action to take. The group deliberated in secret for most of a week. Initially, the experts favored air strikes followed by an invasion, but they felt that would inevitably lead to nuclear war.
Allison said they knew that Soviet-leader Nikita Khrushchev would respond in some forceful way. “So they think he is going to attack U.S. missiles in Turkey - we had missiles there that looked almost exactly like the missiles they were putting in Cuba. And then when they attacked the missiles in Turkey, which were nuclear-warhead armed missiles designed to fire against the Soviet Union, we would obviously have to respond against the Soviet Union,” he said. “So that could have been another path to nuclear war, which was the reason why they rejected that option after they thought about it for a while and chose instead a naval blockade of Cuba.”
Kennedy Opts for Naval Blockade
President Kennedy made the announcement during a televised speech to the nation on October 22nd, 1962. He warned the Soviet leadership, saying, “It shall be the policy of this nation to regard any nuclear missile launched from Cuba against any nation in the Western Hemisphere as an attack by the Soviet Union on the United States, requiring a full retaliatory response upon the Soviet Union.”
Two days later, Soviet ships approached the quarantine line and stopped. Secretary of State Dean Rusk was quoted as saying: “We were eyeball to eyeball and the other fellow just blinked.”
Sergei Khrushchev, son of the Soviet leader, was 27 at the time. He said he remembers his father as being calm throughout the crisis. "He was not panicking. He thought that one of the most important things was not allow to make the first shot,” Khrushchev said. “Because after the first shot, there will be no negotiation and everything would be in the hands of the military who behave in a very different way. And I think President Kennedy had the same idea, to avoid the first shot, because before this you can bargain, after that - you will die."
Khrushchev said his father and President Kennedy were adversaries, but they negotiated with each other.
While the naval quarantine of Cuba worked, tensions rose as Moscow continued to make operational the missiles already in Cuba.
Differing Messages from Khrushchev
On October 26th, 1962, `Kennedy received a message from Khrushchev, offering to withdraw the missiles from Cuba, in exchange for assurances that Washington would neither invade that country nor overthrow Fidel Castro.
Before replying, President Kennedy received - the next day - another letter from Khrushchev. This time the offer was worse: the U.S. must withdraw its missiles from Turkey as a price for Moscow withdrawing its missiles from Cuba.
Graham Allison said Kennedy and his staff decided to ignore the second letter and agreed to incorporate the contents of the first letter in a new proposal.
U.S. Proposal
“And the proposal consists of three components. One is a public deal - and the public deal is basically what the first letter proposed, which is you withdraw the missiles and I will guarantee that we will not invade Cuba or attack Cuba. There is a private ultimatum, and it says we need a response within the next 24 hours or else we are going to act,” said Allison. “And there is a third component - which I call a ‘secret sweetener’ - which says we are not prepared to do a deal with you for the missiles in Turkey. But I’ll just tell you as a fact, if the missiles are withdrawn from Cuba, within six months, there will not be any missiles in Turkey.”
On October 28th, Nikita Khrushchev announced on Radio Moscow the Soviet Union had accepted the American offer and would withdraw its missiles from Cuba.
Blow to Moscow's Prestige?
Sergei Khrushchev said some people saw this as a blow to Moscow’s prestige. “In each bargaining, you have decisions that satisfied you as much as possible and in each case you have the people who will not be satisfied with the thing [decision],” said Khrushchev. “It was in the United States and it was in the Soviet Union too. Especially on our side, there were the Chinese who just hated this feeling, they told us you are scared, you surrendered to the Americans, you have to start the war. All the time, it is those people who are standing aside and they want the other people to start the war.”
By mid-November 1962, all Soviet missiles were out of Cuba. And by next April - as per their secret deal - all U.S. missiles in Turkey were removed.
Graham Allison, an expert on the Cuban Missile Crisis, said there were two types of missiles. “One were medium-range ballistic missiles, which could deliver a nuclear warhead at D.C. [District of Columbia],” he said. “And there were intermediate-range nuclear missiles that could deliver warheads as far as Omaha, [Nebraska], where the Strategic Air Command [was located]. So these covered two-thirds of the United States.”
Allison said the discovery was made by what he called “a magical intelligence capability”. “That an airplane, the U-2, could fly at over 60,000 feet, nobody would know that it was there, over territory, and then with this amazing camera take pictures that gave you details of what was happening on the ground - this was just unimaginable for most people. It was a great American intelligence success because the missiles were discovered before they were operational,” said Allison.
Kennedy Discusses Options
President John F. Kennedy then convened a small group of experts to decide what course of action to take. The group deliberated in secret for most of a week. Initially, the experts favored air strikes followed by an invasion, but they felt that would inevitably lead to nuclear war.
Allison said they knew that Soviet-leader Nikita Khrushchev would respond in some forceful way. “So they think he is going to attack U.S. missiles in Turkey - we had missiles there that looked almost exactly like the missiles they were putting in Cuba. And then when they attacked the missiles in Turkey, which were nuclear-warhead armed missiles designed to fire against the Soviet Union, we would obviously have to respond against the Soviet Union,” he said. “So that could have been another path to nuclear war, which was the reason why they rejected that option after they thought about it for a while and chose instead a naval blockade of Cuba.”
Kennedy Opts for Naval Blockade
President Kennedy made the announcement during a televised speech to the nation on October 22nd, 1962. He warned the Soviet leadership, saying, “It shall be the policy of this nation to regard any nuclear missile launched from Cuba against any nation in the Western Hemisphere as an attack by the Soviet Union on the United States, requiring a full retaliatory response upon the Soviet Union.”
Two days later, Soviet ships approached the quarantine line and stopped. Secretary of State Dean Rusk was quoted as saying: “We were eyeball to eyeball and the other fellow just blinked.”
Sergei Khrushchev, son of the Soviet leader, was 27 at the time. He said he remembers his father as being calm throughout the crisis. "He was not panicking. He thought that one of the most important things was not allow to make the first shot,” Khrushchev said. “Because after the first shot, there will be no negotiation and everything would be in the hands of the military who behave in a very different way. And I think President Kennedy had the same idea, to avoid the first shot, because before this you can bargain, after that - you will die."
Khrushchev said his father and President Kennedy were adversaries, but they negotiated with each other.
While the naval quarantine of Cuba worked, tensions rose as Moscow continued to make operational the missiles already in Cuba.
Differing Messages from Khrushchev
On October 26th, 1962, `Kennedy received a message from Khrushchev, offering to withdraw the missiles from Cuba, in exchange for assurances that Washington would neither invade that country nor overthrow Fidel Castro.
Before replying, President Kennedy received - the next day - another letter from Khrushchev. This time the offer was worse: the U.S. must withdraw its missiles from Turkey as a price for Moscow withdrawing its missiles from Cuba.
Graham Allison said Kennedy and his staff decided to ignore the second letter and agreed to incorporate the contents of the first letter in a new proposal.
U.S. Proposal
“And the proposal consists of three components. One is a public deal - and the public deal is basically what the first letter proposed, which is you withdraw the missiles and I will guarantee that we will not invade Cuba or attack Cuba. There is a private ultimatum, and it says we need a response within the next 24 hours or else we are going to act,” said Allison. “And there is a third component - which I call a ‘secret sweetener’ - which says we are not prepared to do a deal with you for the missiles in Turkey. But I’ll just tell you as a fact, if the missiles are withdrawn from Cuba, within six months, there will not be any missiles in Turkey.”
On October 28th, Nikita Khrushchev announced on Radio Moscow the Soviet Union had accepted the American offer and would withdraw its missiles from Cuba.
Blow to Moscow's Prestige?
Sergei Khrushchev said some people saw this as a blow to Moscow’s prestige. “In each bargaining, you have decisions that satisfied you as much as possible and in each case you have the people who will not be satisfied with the thing [decision],” said Khrushchev. “It was in the United States and it was in the Soviet Union too. Especially on our side, there were the Chinese who just hated this feeling, they told us you are scared, you surrendered to the Americans, you have to start the war. All the time, it is those people who are standing aside and they want the other people to start the war.”
By mid-November 1962, all Soviet missiles were out of Cuba. And by next April - as per their secret deal - all U.S. missiles in Turkey were removed.