The European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA have released the first images from the Solar Orbiter spacecraft — the closest pictures ever taken of the sun.
“These amazing images will help scientists piece together the sun’s atmospheric layers, which is important for understanding how it drives space weather near the Earth and throughout the solar system,” said Holly Gilbert, NASA project scientist.
The two space agencies, working in collaboration, launched the Solar Orbiter in February from Cape Canaveral, and it completed its first close pass of the sun in mid-June. The spacecraft took the pictures approximately 48 million miles from the sun — about half the distance between Earth and the sun.
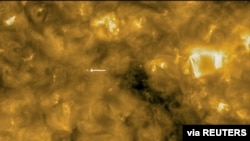
The high-resolution images released Thursday revealed tiny solar flares, what principal investigator David Berghmans called “campfires.”
“These campfires we are talking about here are the little nephews of solar flares, at least a million, perhaps a billion times smaller,” said Berghmans, an astrophysicist at the Royal Observatory of Belgium in Brussels.
“They are literally everywhere we look,” Berghmans said.
The campfires could help explain why the corona, the Sun’s upper atmosphere, is 300 times hotter than the solar surface.
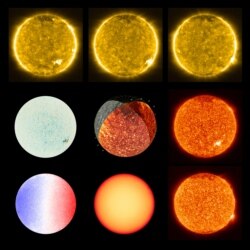
Of the Solar Orbiter’s 10 instruments, six are imaging devices, each studying a different aspect of the sun.
The Solar and Heliospheric Imager (SoloHI) exposed zodiacal light — light from the sun reflecting off interplanetary dust. To capture it, the imager had to dim the sun’s light to one-trillionth of its normal brightness.
The Polar and Helioseismic Imager (PHI) mapped the sun’s magnetic field. Four instruments meant for measuring the space environment immediately surrounding the spacecraft yielded data about the presence of carbon, oxygen, silicon and other heavy ions in the solar wind from the inner heliosphere.
Although the coronavirus pandemic forced mission control at the European Space Operations Center in Germany to close down for more than a week, and all but essential personnel worked from home, the ESA and NASA were ready for the first solar pass in June.
“We didn’t expect such great results so early,” said Daniel Muller, ESA’s Solar Orbiter project scientist. “These images show that the Solar Orbiter is off to an excellent start.”
“This is just the beginning of the long epic journey of Solar Orbiter,” Muller said.