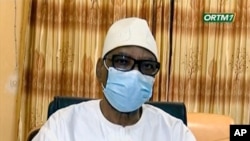
President Ibrahim Boubacar Keita resigned late Tuesday night, hours after he was arrested by mutinous soldiers following months of political turmoil in the West African nation.
Wearing a surgical mask in recognition of the coronavirus pandemic, a weary-looking Keita appeared on state television to announce he was stepping down in order to avoid any bloodshed.
The 75-year-old deposed leader said if “certain elements” of the military wanted to end his presidency with “their intervention, do I really have a choice?” Keita also announced that his government and the National Assembly would be dissolved.
Keita’s resignation speech capped a day of turmoil that began when soldiers seized weapons from an army base in Kati and advanced on the capital of Bamako. A reporter in Mali told VOA’s French to Africa service that the soldiers ““went on the rampage, got to the arsenals, got the guns, started shooting in the air, went out and cut off access to the camp.”
Scores of anti-government protesters gathered in Bamako’s central square to cheer the soldiers on as they made their way to Keita’s house to arrest him.
The soldiers arrested Keita and Prime Minister Boubou Cisse at Keita’s house and drove them back to Kati, the same camp where the 2012 coup that overthrew President Amadou Toumani Toure began. The overthrow of Toure unleashed a violent Islamic insurgency in central Mali, despite the ongoing presence of French troops that initially drove the jihadists out of northern Mali.
No casualties have been reported from Tuesday’s uprising.
Mali has been mired in months of protests led by the main opposition party June 5 Movement over an economic crisis, corruption and Keita’s failure to quell an eight-year-old Islamic insurgency that has gained a foothold in central Mali. Anger also brewed over the results of 31 legislative races held in April that remain in dispute.
Violent clashes between anti-government protesters and security forces last month left at least 14 protestors dead and another 154 injured.
The regional bloc ECOWAS (Economic Community of West African States) crafted a plan for Keita to form a unity government with the opposition, which was rejected by the June 5 Movement.
ECOWAS (Economic Community of West African States) sealed its member states’ borders with Mali after Keita and Cisse’s arrest and suspended all financial transactions between Mali and its 14 other members and is, for now, removing Mali from its decision-making bodies.
ECOWAS officials have called for sanctions on those it calls “putschists and their partners and collaborators.”
J. Peter Pham, the U.S. envoy to the Sahel region, issued a statement saying Washington is opposed to any “extra-constitutional change.”
An African Union Commission spokesman said Chairperson Moussa Faki Mahamat strongly condemns the arrests of Keita and Cisse and strongly rejects any attempted unconstitutional change of government in Mali.
United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres is calling for the immediate restoration of constitutional order and the rule of law in Mali. Council members France and Niger have called for a closed-door meeting of the Security Council Wednesday.